Money has played a pivotal role in human civilization, enabling the exchange of goods and services. Throughout history, money has evolved from primitive bartering systems to sophisticated digital forms and even the emergence of cryptocurrencies. Each stage in the evolution of money represents a significant leap forward, transforming the way we conduct transactions and manage our finances. In this comprehensive blog post, we will explore the various stages of the evolution of money, including the rise of plastic money, digital money, and the advent of cryptocurrencies. We will delve into their time spans, examples, features, and examine the pros and cons associated with each stage.
 |
| The Evolution of Money: From Barter to Digital and Cryptocurrency Subramoneyplanning |
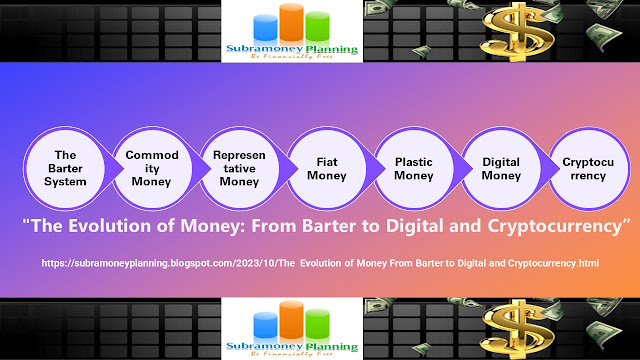
1. The Barter System: The barter system, the earliest form of trade, involved the direct exchange of goods and services without the use of money. In this system, individuals traded items they had in surplus for things they needed. For example, a farmer might exchange his surplus wheat for a blacksmith's tools. While the barter system facilitated basic transactions, it faced challenges such as the "double coincidence of wants" problem, where two parties had to desire each other's goods simultaneously.
2. Commodity Money: Commodity money emerged as a solution to the limitations of bartering. It involved using valuable goods with inherent worth as a medium of exchange. Ancient civilizations, such as the Egyptians and Greeks, used commodities like gold, silver, and even seashells as currency. These commodities held value and were widely accepted. However, carrying large quantities of commodities posed logistical challenges.
3. Representative Money: Representative money replaced commodity money and was backed by a valuable commodity, usually gold or silver. Banknotes were issued by banks, redeemable for a specific amount of the underlying precious metal. This system provided convenience as carrying around heavy gold or silver coins was no longer necessary. An example is the Gold Standard era, where many countries backed their currencies with gold reserves.
4. Fiat Money: Fiat money is the current widely adopted form of currency. It has value because the government declares it as legal tender. Fiat money is not backed by a physical commodity but relies on trust and confidence in the issuing government. An example is the U.S. dollar, which is not redeemable for a specific commodity but is widely accepted as a medium of exchange. Fiat money offers stability, liquidity, and is easily divisible. However, it is susceptible to inflation and the impact of government policies.
5. Plastic Money: Plastic money, represented by credit cards and debit cards, revolutionized financial transactions. Credit cards allow users to make purchases on credit, while debit cards enable direct access to funds in a bank account. Plastic money offers convenience, security, and flexibility in making payments. It eliminates the need for carrying cash, enables online and international transactions, and provides various rewards and benefits. However, plastic money can lead to overspending, debt accumulation, and vulnerability to fraud and identity theft.
6. Digital Money: Digital money refers to electronic forms of payment, such as online banking, electronic fund transfers, and mobile payment apps. It has transformed the way we transact, making it faster, more convenient, and accessible. Digital money allows for seamless transactions, immediate fund transfers, and easy tracking of financial transactions. It enables online shopping, bill payments, and person-to-person transfers with just a few clicks. However, concerns regarding data security, privacy, and the digital divide must be addressed to ensure widespread adoption and inclusivity.
7. Cryptocurrency: Cryptocurrency, such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and many others, represents a decentralized form of digital currency. It is based on blockchain technology, which ensures transparency, security, and immutability of transactions. Cryptocurrencies provide individuals with control over their funds, reduce reliance on intermediaries, and offer the potential for investment growth. However, they are highly volatile, lack widespread acceptance, and face regulatory challenges. Additionally, the complexity of blockchain technology and the potential for fraudulent schemes require users to exercise caution and educate themselves.
 |
The evolution of money showcases the remarkable progress of human civilization and the ingenuity of economic systems. From the barter system to digital currencies and cryptocurrencies, each stage has brought forth new features and challenges. Plastic money has revolutionized transactions, offering convenience and accessibility. Digital money has expanded financial inclusion and efficiency. Cryptocurrencies have introduced decentralized control and potential for investment growth. However, each form of money comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
Understanding the evolution of money is crucial in adapting to the changing financial landscape. It empowers individuals to make informed decisions, utilize various payment methods responsibly, and navigate the complexities of the modern economy. As technology continues to advance, the future of money holds the promise of further innovation and transformation, shaping the way we transact, invest, and store value. By embracing these advancements while being mindful of the risks, we can make the most of the evolving financial landscape for a prosperous future.






0 comments:
Post a Comment